41+ Actin And Myosin Diagram
Understand the role of ATP hydrolysis in this process. Web The thin actin filaments also have binding sites for the myosin headsa cross-bridge forms when a myosin head binds with an actin filament.
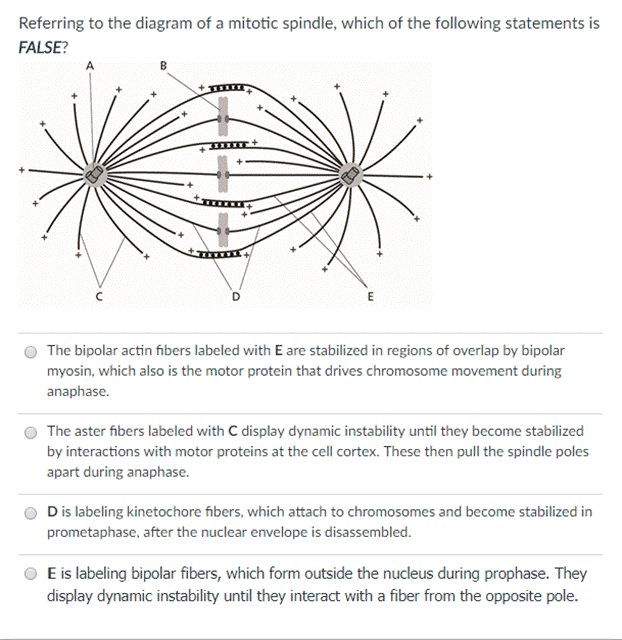
Get Answer Referring To The Diagram Of A Mitotic Spindle Which Of The Transtutors
Web Ca 2 rushes out of the SR where it is available to troponin-c.

. The molecular mechanism involves structural transitions at. Web A High resolution ribbon diagram of chicken S-1 myosin determined using X-ray crystallography. Web Each myosin head also called subfragment-1 S1 is composed of a motor domain that contains the actin and adenosine triphosphate ATP-binding region and an elongated.
Web In muscles projections on the myosin filaments the so-called myosin heads or cross-bridges interact with the nearby actin filaments and in a mechanism powered. As for other nanomotors. This is a key part of how.
This is a well labelled. Web Supporting muscle contractions as actin filaments slide alongside myosin filaments. Web There are six actin molecules around a single myosin molecules and there are more than 100000 sarcomeres one myosin and six actin make 1 sarcomere in a single bicep.
In muscle actin molecules twist together to form a thin filament which. Web Myosin via its cyclic interactions with actin filaments is a superfamily of molecular motor proteins that powers movement on actin filaments in all eukaryotic cells. This is a well labelled diagram of Structure of myofibrils.
Troponin-C bound to Ca 2 shifts the tropomyosin away from the actin filament and the myosin. Web In this chapter we will characterize the structural and biochemical basis of the actin-myosin interaction and explain its relationship with myosins cellular roles with emphasis on the. Web Class I myosins are the largest group of unconventional myosins 56 and are characterized by three domains.
Web The Product Release Steps on Actin. In contrast myosin is a protein that produces. An actin-binding head that hydrolyses ATP to move.
Labeled are the key features of the molecule the ATP and actin binding. Web 1 day agoAbstract. Web This is the well labelled diagram of structure of Actin Filament And Myosin Monomer.
Web These papers described the position of myosin and actin filaments at various stages of contraction in muscle fibers and proposed how this interaction produced contractile force. Myosin VI Myo6 is the only minus-end directed nanomotor on actin allowing it to uniquely contribute to numerous cellular functions. Web The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin is a protein that produces thin contractile filaments within muscle cells.
Actin-myosin interactions play crucial roles in the generation of cellular force and movement. After hydrolysis of ATP by myosin force is produced upon sequential conformational changes of the motor triggered by rebinding to F-actin. Web Learn how proteins specifically myosin and actin use ATP to produce movement in muscles.
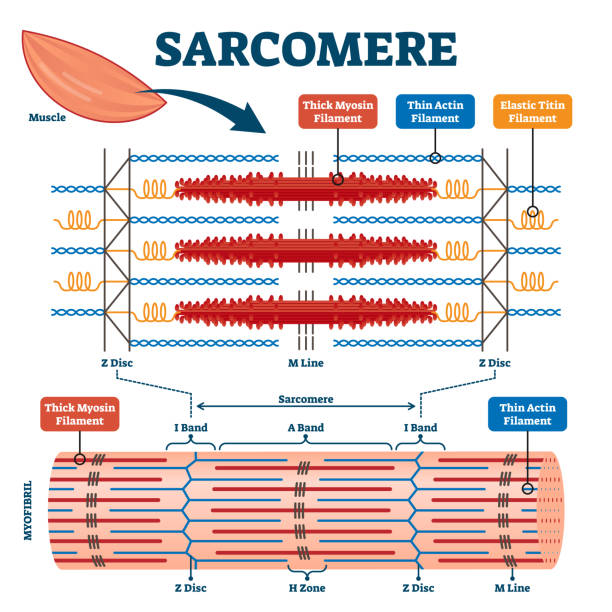
50 Myosin Illustrations Royalty Free Vector Graphics Clip Art Istock Actin Myosin Myosin Head Cardiac Myosin

Pin On Microbiology Notes
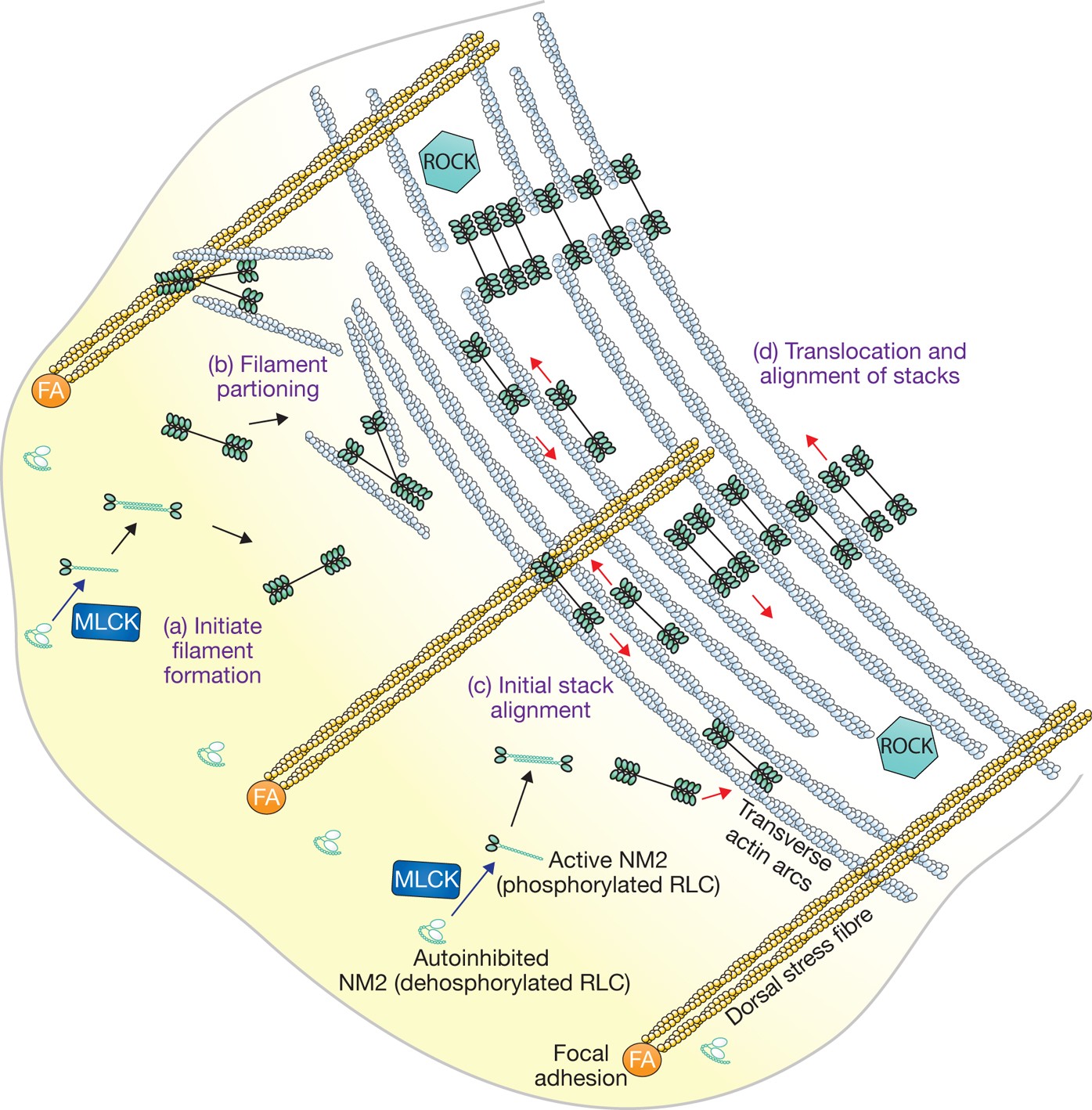
Growing Splitting And Stacking Myosin Ii Filaments Nature Cell Biology

Schematic Of Proposed Myosin Thick And Actin Thin Filament Sliding Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Illustration Of A Sarcomere Top With Actin Myosin And Download Scientific Diagram

Arrangement Of Actin Filaments In Pseudopodia According To Refs Download Scientific Diagram
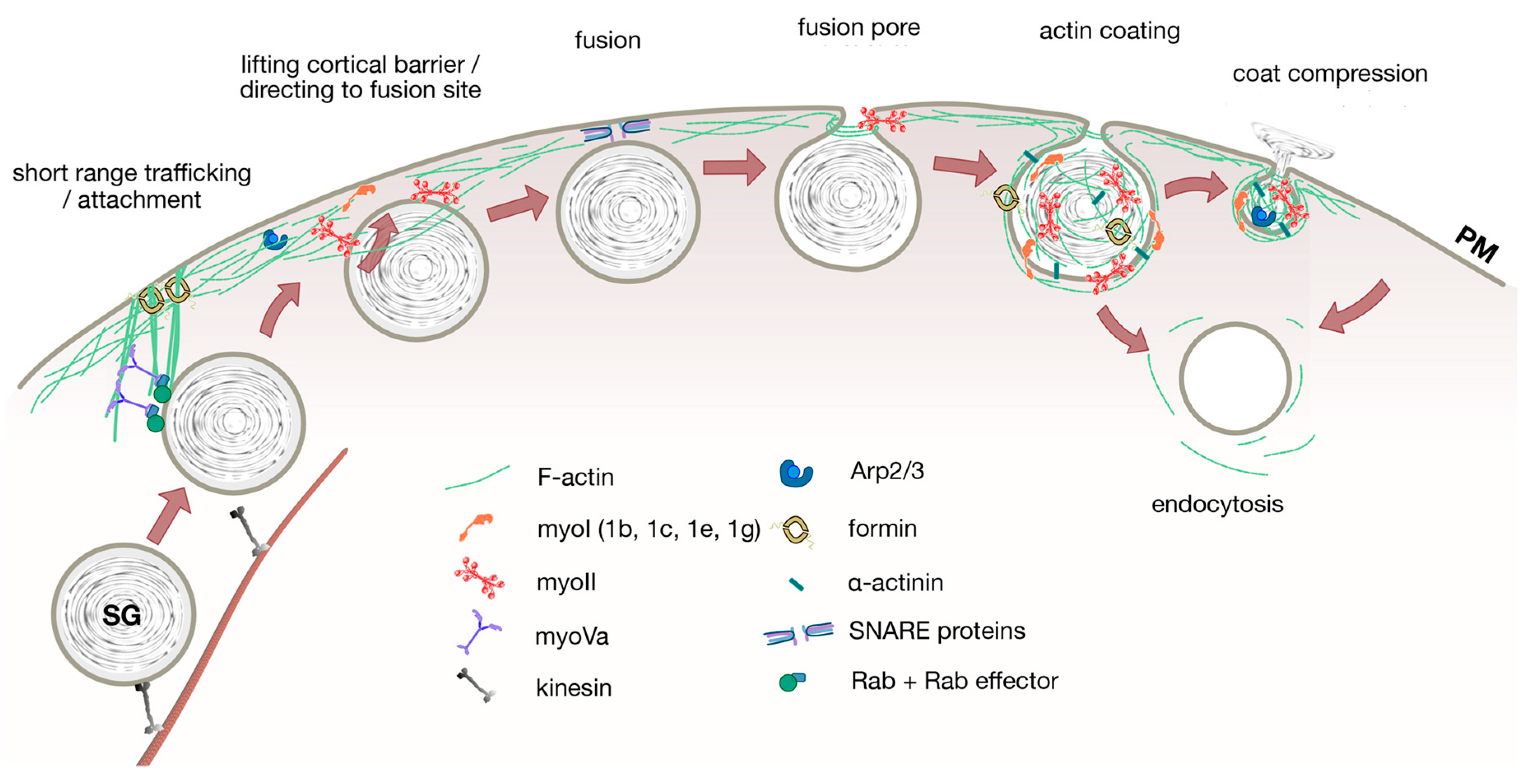
Cells Free Full Text Actin And Myosin In Non Neuronal Exocytosis

Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction Cbse Class 11

Actin And Myosin Myofilaments Part 4 Diagram Quizlet
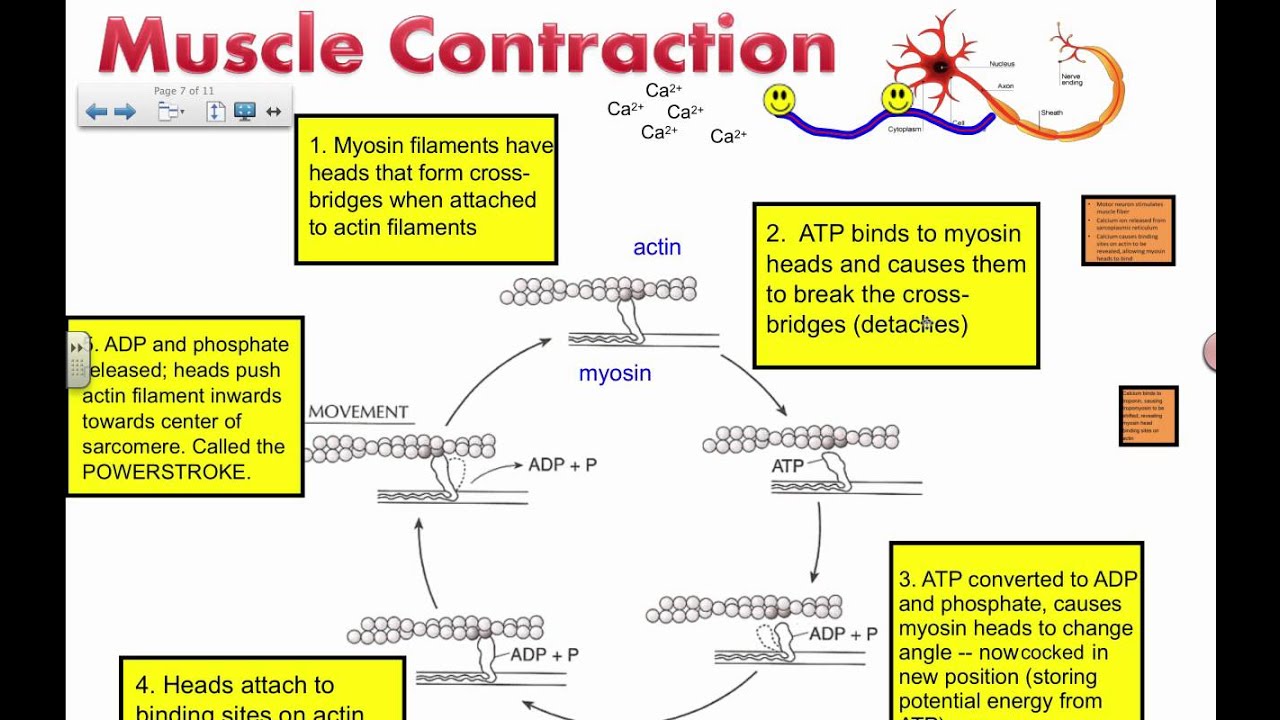
Muscle Contraction Actin And Myosin Ib Biology Youtube

Sliding Filament Theory Labster Theory

Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary
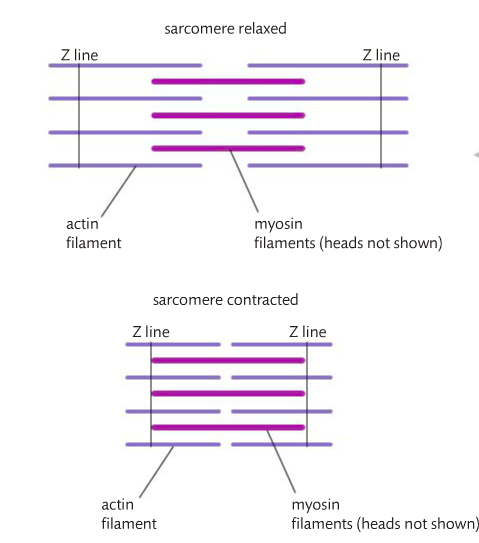
11 2 Movement The Mad Scientist

Schematic Diagram Of Smooth Muscle Length Tension Curve Myosin Actin Download Scientific Diagram
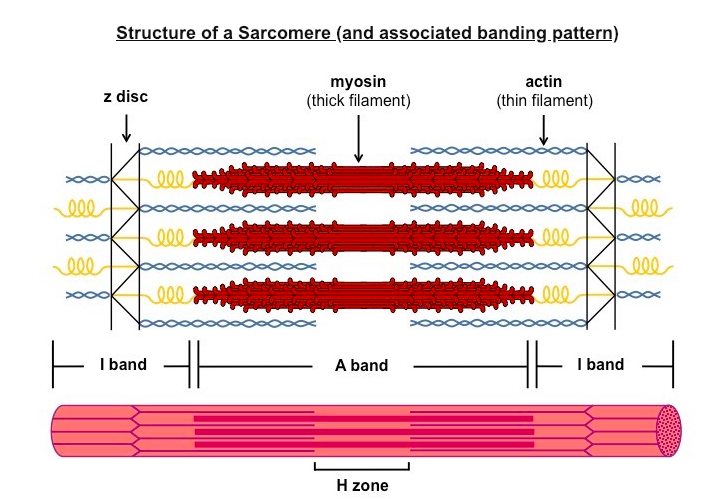
11 2 Movement The Mad Scientist

File Myosin Filament Jpg Wikimedia Commons

How Myosin Generates Force On Actin Filaments Trends In Biochemical Sciences